Answer:
The gravitational force will be closest to group A: 56 N.
Step-by-step explanation:
The gravitational force of the planet is given by:
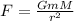
Where:
G: is the gravitational constant
m: is the mass of the object
M: is the mass of the planet
r: is the distance
When the object is 500 km above the surface of the planet, the gravitational force is 100 N:
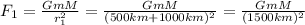
And when the object is 500 km farther from the planet, the gravitational force is given by:
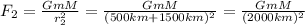
By dividing F₂ by F₁ we can calculate F₂:
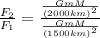
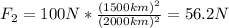
Therefore, the gravitational force will be closest to group A: 56 N.
I hope it helps you!