Answer:
S = {(0, 5), (0, - 5), (3, 4), (3, -4), (-3, 4), (-3, -4), (4, 3), (4, -3), (-4, 3), (-4, -3), (5,0), (-5, 0) }
Explanation:
Remember that the distance between two points (a, b) and (c, d) is given by:
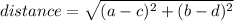
So, here we have that the distance between the point (x, y) and the origin, (0, 0) must have a magnitude of 5 units, then we want to solve:
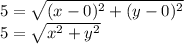
If we square both sides, we get
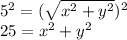
Now we want to find all the points (x, y) that meet this condition, suc that:
x ∈ Z
y ∈ Z
So both x and y must be integers.
So here we can just play with different values of x and y.
For example, if we define:
x = 0 we get:
25 = 0^2 + y^2
25 = y^2
√25 = y
Then we can have y = 5 or y = -5
from this we got two points:
(0, 5) and (0, - 5)
if x = 1 we have:
25 = 1^2 + y^2
25 - 1 = y^2
24 = y^2
There is no integer such that its square is equal to 24, so we can stop here.
if x = 2 or - 2, we have:
25 = 2^2 + y^2
25 = 4 + y^2
25 -4 = 21 = y^2
Again, there is no integer such that its square is equal to 21, so we can stop here.
if x = +3 or -3, we have:
25 = 3^2 + y^2
25 = 9 + y^2
25 - 9 = 16 = y^2
√16 = y
then we can have y = 4 or y = -4
from this we got four points:
(3, 4)
(-3, 4)
(3, -4)
(-3, -4)
And for symmetry, if x = 4 or -4 we have the points:
(-4, 3)
(4, 3)
(-4, -3)
(4, -3)
finally, again for symmetry, if we take x = 5 or x = -5 we have the points:
(5,0)
(-5, 0)
Concluding, the set of all possible values (x, y) is:
S = {(0, 5), (0, - 5), (3, 4), (3, -4), (-3, 4), (-3, -4), (4, 3), (4, -3), (-4, 3), (-4, -3), (5,0), (-5, 0) }