The magnitude of the acceleration of the suspended block as it falls is 3.4 m/
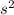 (approximately).
(approximately).
The magnitude of the acceleration of the suspended block as it falls can be determined using the formula:
acceleration = g * (sin(θ) -
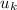 * cos(θ))
* cos(θ))
Where,
g is the acceleration due to gravity
θ is the angle of the incline
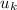 is the coefficient of kinetic friction.
is the coefficient of kinetic friction.
In this case, since there is no pulley mass or friction in the pulley, the acceleration will be solely determined by the angle of the incline and the coefficient of kinetic friction.
By substituting the given values, the magnitude of the acceleration of the suspended block can be calculated as:
acceleration = g * (sin(θ) -
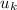 * cos(θ))
* cos(θ))
= 9.8 * (sin (21.7) - 0.4 * cos (21.7))
= 3.4 m/
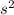 (approximately)
(approximately)