Answer: The equations in column A is matched with gas laws in column B as follows:
21. PV = nRT : (g) Ideal gas law
22.
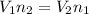 : (f) Avogadro's law
: (f) Avogadro's law
23.
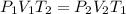 : (e) Combined Gas Law
: (e) Combined Gas Law
24.
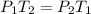 : (d) Gay-Lusaac's law
: (d) Gay-Lusaac's law
25.
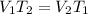 : (c) Charles' law
: (c) Charles' law
26.
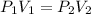 : (b) Boyle's law
: (b) Boyle's law
27.
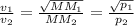 : (a) Graham's Law of effusion
: (a) Graham's Law of effusion
Step-by-step explanation:
(A) Ideal gas law: It states that the product of pressure and volume is directly proportional to the product of number of moles and temperature.
So, PV = nRT
where,
P = pressure
V = volume
n = no. of moles
R = gas constant
T = temperature
- Boyle's law: At constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to volume.
So,
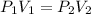
- Charles' law: At constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to temperature. So,
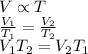
- Gay-Lussac's law: At constant volume, the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to temperature.
So,
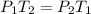
- Avogadro's law: At same temperature and pressure, the volume of gas is directly proportional to moles of gas.
So,
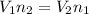
- Combined gas law: When Boyle's law, Charles' law, and Gay-lussac's law are combined together then it is called combined gas law. So,
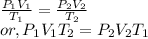
- Graham's law of effusion: It states that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of mass of its particles.
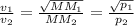
Thus, we can conclude that equation in column A is matched with gas laws in column B as follows:
21. PV = nRT : (g) Ideal gas law
22.
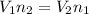 : (f) Avogadro's law
: (f) Avogadro's law
23.
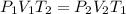 : (e) Combined Gas Law
: (e) Combined Gas Law
24.
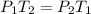 : (d) Gay-Lusaac's law
: (d) Gay-Lusaac's law
25.
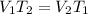 : (c) Charles' law
: (c) Charles' law
26.
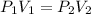 : (b) Boyle's law
: (b) Boyle's law
27.
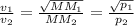 : (a) Graham's Law of effusion
: (a) Graham's Law of effusion