Answer:
The apparent
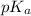 value for aspartic acid increases.
value for aspartic acid increases.
Step-by-step explanation:
The
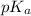 value of an ionizable group is influenced by its surrounding environment. When two similar charges are close to each other, they tend to repel, and when opposite charges are close, they tend to attract.
value of an ionizable group is influenced by its surrounding environment. When two similar charges are close to each other, they tend to repel, and when opposite charges are close, they tend to attract.
If a neighbouring carboxylic acid is close to the side chain of aspartic acid (which also has a carboxylic acid), there would be repulsion between the negatively charged carboxylate ions when deprotonated. This repulsion would make it less favourable for both groups to be deprotonated simultaneously.
Therefore, the presence of a neighbouring carboxylic acid would make the aspartic acid side chain less likely to lose its proton, effectively increasing its
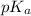 value.
value.
Thus, the correct statement is:
The apparent
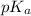 value for aspartic acid increases.
value for aspartic acid increases.