Answer:
The
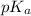 of the side chain may be lower or higher in a polypeptide chain due to differences in their microenvironments.
of the side chain may be lower or higher in a polypeptide chain due to differences in their microenvironments.
Step-by-step explanation:
The
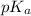 values of ionizable side chains can vary depending on whether the amino acid is free or is part of a polypeptide chain. This variation is primarily due to the microenvironment in which the side chain finds itself when it's part of a larger protein structure.
values of ionizable side chains can vary depending on whether the amino acid is free or is part of a polypeptide chain. This variation is primarily due to the microenvironment in which the side chain finds itself when it's part of a larger protein structure.
In a polypeptide chain, the side chain's
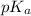 can be influenced by several factors:
can be influenced by several factors:
1. Proximity to other charged residues which can either stabilize or destabilize the ionized form of the side chain.
2. The hydrophobic or hydrophilic environment in which the side chain resides, which can affect its tendency to gain or lose a proton.
3. Hydrogen bonding with neighboring residues.
4. The overall three-dimensional structure of the protein, which might position the side chain in a more exposed (to the solvent) or more buried position.
Given these considerations, the correct statement is:
The
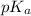 of the side chain may be lower or higher in a polypeptide chain due to differences in their microenvironments.
of the side chain may be lower or higher in a polypeptide chain due to differences in their microenvironments.