Final Answer:
The identification of whether a molecule is polar or non-polar depends on its molecular geometry and the presence of polar bonds. Drawing the structural formula for each molecule and considering the molecular shapes,
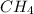 (methane) is non-polar, while
(methane) is non-polar, while
 (water) is polar.
(water) is polar.
Step-by-step explanation:
In the structural formula of
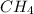 , the carbon atom forms four single bonds with four hydrogen atoms, creating a tetrahedral molecular shape. As the four hydrogen atoms are identical and have equal electronegativity, there is no net dipole moment, resulting in a non-polar molecule.
, the carbon atom forms four single bonds with four hydrogen atoms, creating a tetrahedral molecular shape. As the four hydrogen atoms are identical and have equal electronegativity, there is no net dipole moment, resulting in a non-polar molecule.
In contrast,
 has a bent molecular shape due to the presence of two lone pairs on the oxygen atom. The oxygen-hydrogen bonds are polar, and the asymmetry of the molecule leads to a net dipole moment, making
has a bent molecular shape due to the presence of two lone pairs on the oxygen atom. The oxygen-hydrogen bonds are polar, and the asymmetry of the molecule leads to a net dipole moment, making
 a polar molecule.
a polar molecule.
The polarity of a molecule is determined by the distribution of electron density and the electronegativity of its constituent atoms. In the case of
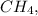 the symmetrical arrangement of atoms results in a balanced distribution of electron density, leading to a non-polar molecule. However, in
the symmetrical arrangement of atoms results in a balanced distribution of electron density, leading to a non-polar molecule. However, in
 , the oxygen atom attracts electrons more strongly than hydrogen, creating a polar covalent bond.
, the oxygen atom attracts electrons more strongly than hydrogen, creating a polar covalent bond.
The molecular geometry and the presence of polar bonds contribute to the overall polarity of the molecule. Understanding molecular polarity is crucial for predicting physical properties and interactions in chemical systems.