Final Answer:
The sum
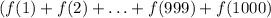 evaluates to -6.
evaluates to -6.
Explanation:
Let's break down the expression for ( f(x) ).
![\[ f(x) = \lfloor 2 - (3x)/(x + 3) \rfloor \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/2xgw062et1i20o55rt4w6p79dsh2mqiofm.png)
To simplify the expression inside the floor function, we first combine the terms:
![\[ f(x) = \lfloor (2x + 6 - 3x)/(x + 3) \rfloor \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/456tuiosnakn9ikk7gjyxu9h4ovqqo8moo.png)
![\[ f(x) = \lfloor (6 - x)/(x + 3) \rfloor \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/itkzv0sfh8dap31lpsbni1vaaqfh0pqr4e.png)
Now, let's analyze the expression
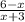 :
:
1. If ( x < 6 ), then
 , and
, and
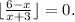
2. If ( x = 6 ), then
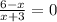 , and
, and
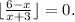
3. If
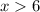 , then
, then
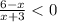 , and
, and
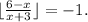
Now, consider the values of ( x ) in the given range (1 to 1000):
1. For ( x = 1 ) to ( x = 6 ), ( f(x) = 0 ).
2. For ( x = 7 ) to ( x = 1000 ), ( f(x) = -1 ).
So, the sum \( f(1) + f(2) + \ldots + f(999) + f(1000) \) is equivalent to the sum of 994 zeros and 6 -1's:
![\[ 994 * 0 + 6 * (-1) = 0 - 6 = -6 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/8x0pnrxaq40p12zyab7z0kjql29sap6foa.png)
Therefore, the value of the given sum is -6.