Answer:
So, the outlet temperature of the water is approximately 92°C.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the outlet temperature of the water, we can use the concept of heat transfer in a pipe. The heat transferred to the water will cause its temperature to rise from the inlet temperature to the outlet temperature.
We can use the following formula for heat transfer:
![\[Q = m \cdot c \cdot \Delta T\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/college/9h803kck7rvwlq6k5h8oz5o3puvxa4jwyy.png)
Where:
-
 is the heat transfer (in joules).
is the heat transfer (in joules).
-
 is the mass flow rate of water (in kilograms per second).
is the mass flow rate of water (in kilograms per second).
-
 is the specific heat capacity of water (approximately 4,186 J/(kg·K) at room temperature).
is the specific heat capacity of water (approximately 4,186 J/(kg·K) at room temperature).
-
 is the change in temperature (in kelvin or degrees Celsius).
is the change in temperature (in kelvin or degrees Celsius).
First, let's calculate the heat transfer
 .
.
Given:
- Mass flow rate
 = 2 kg/s
= 2 kg/s
- Inlet temperature
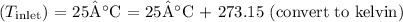
- Surface temperature of the pipe (\(T_{\text{surface}}\)) = 90°C = 90°C + 273.15 (convert to kelvin)
Now, calculate the change in temperature
 :
:
![\[\Delta T = T_{\text{surface}} - T_{\text{inlet}}\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/college/o1jbi4lyvhn77gwqs0pzkknqawfltp7ntt.png)
![\[\Delta T = (90°C + 273.15 K) - (25°C + 273.15 K) = 365.15 K - 298.15 K = 67 K\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/college/yztvgsv7ykxqbhroe112063y157cz0h35e.png)
Now, calculate the heat transfer
 using the formula:
using the formula:
![\[Q = m \cdot c \cdot \Delta T\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/college/9h803kck7rvwlq6k5h8oz5o3puvxa4jwyy.png)
![\[Q = (2 kg/s) \cdot (4,186 J/(kg·K)) \cdot 67 K = 561,784 J/s = 561,784 W (watts)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/college/nbfmk0p4w8ik3vh3r8hhn1ntm8rvfvh2to.png)
Now that we have calculated the heat transfer
 , we can use it to find the outlet temperature
, we can use it to find the outlet temperature
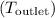 using the same formula:
using the same formula:
![\[Q = m \cdot c \cdot \Delta T\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/college/9h803kck7rvwlq6k5h8oz5o3puvxa4jwyy.png)
![\[\Delta T = (Q)/(m \cdot c)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/college/6337uaioetoxt6ikkdgs707wf1lq01vee8.png)
![\[\Delta T = (561,784 J/s)/((2 kg/s) \cdot (4,186 J/(kg·K))) \approx 67 K\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/college/z7sk1575uxpinbiy9l8v0bxzx7vebwks96.png)
Now, add this change in temperature to the inlet temperature to find the outlet temperature:
![\[T_{\text{outlet}} = T_{\text{inlet}} + \Delta T\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/college/q8fx7onjhpt0xk3tnsq2n7hj1h20nfatvo.png)
![\[T_{\text{outlet}} = (25°C + 273.15 K) + 67 K = 365.15 K\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/college/mk674jlgamcf9n2g5fmlpt6qm05cndiv9q.png)
Convert the outlet temperature from kelvin to degrees Celsius:
![\[T_{\text{outlet}} = 365.15 K - 273.15 K = 92°C\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/college/xfkq6efbn0ws6lizxcd1lergycnidweaac.png)
So, the outlet temperature of the water is approximately 92°C.