Answer:
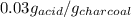
Step-by-step explanation:
The amount adsorbed (solute) is the acetic acid, and the adsorbent is the activated charcoal. The mass of the adsorbent is 10 g.
So, we need to calculate the mass of the acetic acid as follows:
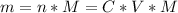
Where:
n: is the number of moles = C*V
M: is the molecular mass = 60.052 g/mol
C: is the final concentration of the acid = 0.5*0.2 mol/L = 0.10 mol/L
V: is the volume = 50 ml = 0.050 L
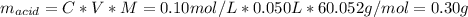
Now, the amount of solute adsorbed per gram of the adsorbent is:
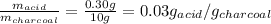
Therefore, the amount of solute adsorbed per gram of the adsorbent is 0.03 g/g.
I hope it helps you!