Answer: 0.926 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
We're given a mass of CO₂ in g, volume in L, and temperature in ⁰C, and looking for the pressure. We'll use the ideal gas law, PV = nRT, and R is the gas constant, and it's 0.08206 L x atm/K x mol⁻¹. n is the number of moles of the gas, and we can calculate the number of moles of CO₂ gas by converting the g of CO₂ gas to moles using its molar mass, 44.01g/mol.
3.67g CO₂(
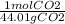 ) = 0.0834 mol CO₂ = n
) = 0.0834 mol CO₂ = n
Next, we need to convert our temperature from ⁰C to K by adding 273.15:
65⁰C + 273.15 = 338.15K
Now, we plug in our known values, V, n, R, and T, into the equation:
P(2.50L) = (0.0834 mol CO₂)(
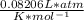 )(338.15K)
)(338.15K)
Now, solve for P:
P(2.50L) = (0.0834 mol CO₂)(
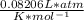 )(338.15K)
)(338.15K)
P(2.50L) = 2.314 L x atm
P =
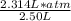
= 0.926 atm
I hope this helps! :)