The water solubility of benzoic acid is approximately
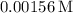 at 25°C.
at 25°C.
To find the water solubility of benzoic acid
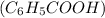 at 25°C, we'll follow these steps:
at 25°C, we'll follow these steps:
1. Determine the concentration of
 ions:
ions:
![\[ \text{pH} = -\log[H^+] \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/o9kdbbw7ccwmbgw7pja3lpuf23kentq9we.png)
![\[ [H^+] = 10^{-\text{pH}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/m1m402g92js77gtrjw0p404dl7o4u8xfew.png)
![\[ [H^+] = 10^(-2.80) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/o0jlsifggyyb68p91olmjiasdirf42mqha.png)
2. Set up the equilibrium expression using the given
 value:
value:
![\[ K_a = ([C_6H_5COO^-][H^+])/([C_6H_5COOH]) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/8qf1oedusg0mp1uz3ujqs9bd1ibjgrgbqb.png)
3. Let x be the concentration of
 ions and
ions and
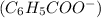 at equilibrium. The initial concentration of benzoic acid
at equilibrium. The initial concentration of benzoic acid
![\([C_6H_5COOH]_0\)](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/sv52g00fdr05sy9brxgujv4p03kk7jyxga.png) is the solubility we are trying to find.
is the solubility we are trying to find.
![\[ 6.4 * 10^(-5) = (x^2)/([C_6H_5COOH]_0) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/v6j07sdkupzjsr9yejxca2a258phqz699c.png)
4. Solve for \([C_6H_5COOH]_0\):
![\[ [C_6H_5COOH]_0 = (x^2)/(6.4 * 10^(-5)) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/n0976ljyorh1i2xgus339bsxn6jiqfhdbt.png)
Since
![\(x = [H^+]\),](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/bsml44j0g8vyn3ir5k3jhf7w1ze62y1yem.png) we can substitute
we can substitute
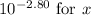 .
.
![\[ [C_6H_5COOH]_0 = ((10^(-2.80))^2)/(6.4 * 10^(-5)) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/b6d641jd7ahhm9wvtwpelwfs4ryzzkde1y.png)
![\[ [C_6H_5COOH]_0 = (10^(-5.60))/(6.4 * 10^(-5)) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/hbb33m0xnc8w4vos1c0lrijjpu2fxxme80.png)
![\[ [C_6H_5COOH]_0 = (1)/(640) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/w3242abvd2olz0fmjq0h9xc9b2zge925ac.png)
![\[ [C_6H_5COOH]_0 = 0.0015625 \, \text{M} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/dp7y4mkbub6j53d4o7oru4g6ekdo6vblc4.png)
So, the water solubility of benzoic acid is approximately
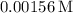 at 25°C.
at 25°C.