Final answer:
The most likely standard voltage change for the ½
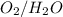 redox pair is +1.23 V.
redox pair is +1.23 V.
Step-by-step explanation:
The most likely standard voltage change for the ½
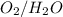 redox pair is +1.23 V (option b).
redox pair is +1.23 V (option b).
The standard electrode (reduction) potentials of the two half-reactions indicate that water may be oxidized at a less negative/more positive potential than chloride ion. Therefore, water is more readily oxidized. In practice, both water and chloride ion are oxidized under typical conditions, producing a mixture of oxygen and chlorine gas.
Based on the information provided, the most likely standard voltage change for the ½
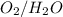 redox pair is +1.23 V. Understanding the standard voltage change for redox pairs is crucial in predicting the feasibility of electrochemical reactions, and in this context, the positive standard voltage change of +1.23 V suggests the thermodynamic favorability of the ½ O2/H2O redox pair, highlighting its potential significance in various electrochemical processes.
redox pair is +1.23 V. Understanding the standard voltage change for redox pairs is crucial in predicting the feasibility of electrochemical reactions, and in this context, the positive standard voltage change of +1.23 V suggests the thermodynamic favorability of the ½ O2/H2O redox pair, highlighting its potential significance in various electrochemical processes.