Answer:
Magnesium is the limiting reactant.
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced reaction is:
2 Mg + O₂ ⇒ 2 MgO
By stoichiometry of the reaction (that is, the relationship between the amount of reagents and products in a chemical reaction), the following quantities participate in the reaction:
- Mg: 2 moles
- O₂: 1 mole
- MgO: 2 moles
Being the molar mass:
- Mg: 24.31 g/mole
- O₂: 32 g/mole
- MgO: 40.31 g/mole
Then the following quantities of mass participate in the reaction:
- Mg: 2 moles* 24.31 g/mole= 48.62 g
- O₂: 1 mole* 32 g/mole= 32 g
- MgO: 2 moles* 40.31 g/mole= 80.62 g
The limiting reagent is one that is consumed first in its entirety, determining the amount of product in the reaction. When the limiting reagent is finished, the chemical reaction will stop.
To determine the limiting reagent, it is possible to use the reaction stoichiometry of the reaction. You can use a simple rule of three as follows: If by stoichiometry of the reaction 32 grams of oxygen react with 48.62 grams of magnesium, 12.5 g of oxygen will act with how much mass of magnesium?
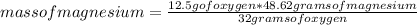
mass of magnesium= 18.99 grams
But 18.99 grams of magnesium are not available, 3.80 molesgrams are available. Since you have less mass than you need to react with 12.5 grams of oxygen, magnesium will be the limiting reagent.