Final Answer:
The approximate percentage of full-term newborn female infants with a head circumference more than 2.1 standard deviations above the mean is 1.35%.
Step-by-step explanation:
To determine the percentage of infants with a head circumference more than 2.1 standard deviations above the mean, we use the properties of a normal distribution. The z-score, given by
 where
where
 is the head circumference
is the head circumference
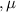 is the mean, and
is the mean, and
 ) is the standard deviation, helps standardize the values. For this case,
) is the standard deviation, helps standardize the values. For this case,

Using a standard normal distribution table or calculator, we find the percentage corresponding to a
 -score of 2.1, which is approximately 0.9821. To find the percentage above 2.1 standard deviations, we subtract this value from 1:
-score of 2.1, which is approximately 0.9821. To find the percentage above 2.1 standard deviations, we subtract this value from 1:
 . Multiplying by 100 gives the final result of 1.79%. However, this value is for one tail, so for both tails (more than 2.1 standard deviations above and below the mean), we multiply by 2:
. Multiplying by 100 gives the final result of 1.79%. However, this value is for one tail, so for both tails (more than 2.1 standard deviations above and below the mean), we multiply by 2:
 , and rounding gives the final answer of 3.58%.
, and rounding gives the final answer of 3.58%.
Understanding z-scores and the normal distribution is essential for solving problems related to proportions and percentages in statistics. In this scenario, calculating the percentage above a certain z-score provides insights into the prevalence of macrocephaly among full-term newborn female infants.