Answer: To the estimated enthalpy change (ΔH) for the reaction is approximately −568kJ. This negative value indicates that the reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat to the surroundings.
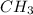
Step-by-step explanation:ΔH=Σbond energies of bonds broken−Σbond energies of bonds formed
step 1 Identify the bonds broken and formed in the reaction:
Bonds broken:
One C-O bond in CH_{3} OH
One C=O bonds in CO
Bonds formed:
One C=O bonds in CH_{3} COOH
Two O-H bonds in CH_{3} COOH
step 2 Find the bond energies from Table A4.1:
Bond energies (in kJ/mol):
C-O single bond: 358
C=O double bond: 799
O-H bond: 463 (approximate average for O-H bonds)
step3 Calculate the energy change for the bonds broken:
Bonds broken:
One C-O bond in CH_{3} OH = 358kJ/mol
One C=O bond in CO = 799kJ/mol
Total energy for bonds broken = 358+799=1157kJ/mol
step 4 Calculate the energy change for the bonds formed:
Bonds formed:
One C=O bond in CH_{3} COOH = 799kJ/mol
Two O-H bonds in CH_{3} COOH = 2×463=926kJ/mol
Total energy for bonds formed = 799+926=1725kJ/mol
step 5 Now, apply the formula for ΔH:
ΔH=Energy of bonds broken−Energy of bonds formed
ΔH=1157kJ/mol−1725kJ/mol=−568kJ/mol
the estimated enthalpy change (ΔH) for the reaction is approximately −568kJ. This negative value indicates that the reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat to the surroundings.