Answer:
(a)
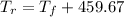
(b)
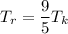
Step-by-step explanation:

a. Relating the Rankine scale to the Fahrenheit scale:

The Rankine scale and the Fahrenheit scale both use the same interval or unit size. However, their zero points are different. Absolute zero on the Rankine scale is
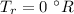 , and absolute zero on the Fahrenheit scale is
, and absolute zero on the Fahrenheit scale is
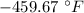 .
.
The relationship between the Rankine and Fahrenheit scales can be derived based on their respective zero points and interval sizes.
Formula:
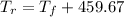
Where:
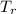 is the temperature in degrees Rankine.
is the temperature in degrees Rankine.
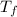 is the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit.
is the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit.

b. Relating the Rankine scale to the Kelvin scale:

The Kelvin scale also has its zero point set at absolute zero, just like the Rankine scale. However, the Kelvin scale uses Celsius-sized intervals, which means the relationship between Kelvin and Rankine involves a conversion factor.
To relate the Rankine and Kelvin scales, we must account for the difference in interval size between the two scales.
Formula:
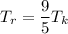
Where:
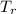 is the temperature in degrees Rankine.
is the temperature in degrees Rankine.
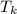 is the temperature in Kelvin.
is the temperature in Kelvin.


Additional Information:
Absolute Zero: The lowest possible temperature where nothing could be colder, and no heat energy remains in a substance. It is the point at which the fundamental particles of nature have minimal vibrational motion.
Rankine Scale (R): A temperature scale based on the Fahrenheit degree but with its zero point set at absolute zero. It is mainly used in engineering systems, especially in the United States.
Kelvin Scale (K): The primary unit of temperature measurement in the physical sciences. Zero on the Kelvin scale is absolute zero, but the Kelvin unit interval is the same as the degree Celsius.
Conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius: The relationship between Fahrenheit (
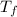 ) and Celsius (
) and Celsius (
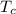 ) temperatures can be given as:
) temperatures can be given as:
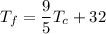
This is useful to know because the Kelvin scale uses Celsius-sized intervals.