Answer:
The last option, ΔT = 30.6 °C
Step-by-step explanation:
The change in temperature of a 200.0 g copper wire, after losing 2350 J of heat upon being removed from the electrical grid, can be determined using the specific heat of copper.
In this scenario, we're dealing with heat transfer and temperature change in a copper wire. Heat transfer occurs when there is a difference in temperature between an object and its surroundings, leading to the flow of thermal energy. The specific heat of a substance measures how much energy is required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of that substance by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin).
Given that the specific heat of copper is provided as 0.38452 J/g°C, we can use the formula:
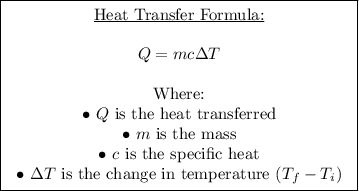
In our case, we are given:
We want to find:

Start by rearranging the heat formula. Solving for 'ΔT':

Substitute in the given values and calculate 'ΔT':
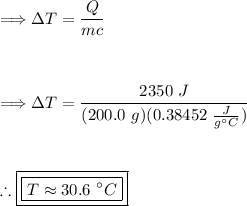
Therefore, the change in temperature of the copper wire is approximately 30.6 °C. Thus, the last option is correct.