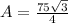The correct exact area of the region common to r=5 and r=10sin(θ) is
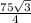
To find the area of the region common to r=5 and r=10sin(θ), we need to set these two equations equal to each other and find the values of θ where they intersect.
5=10sin(θ)
Divide both sides by 10:
sin(θ)= 1/2
This occurs when θ= π/6 or θ= 5π/6 (and their coterminal angles).
Now, set up the integral to find the area between the curves:
![A=(1)/(2) \int_(\theta_1)^(\theta_2)\left[r_2(\theta)^2-r_1(\theta)^2\right] d \theta](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/1ot7hpodi8yg38yyrkxbr00ajr7oqgmrlz.png)
In this case,
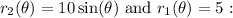
![\begin{aligned}& A=(1)/(2) \int_(\theta_1)^(\theta_2)\left[(10 \sin (\theta))^2-5^2\right] d \theta \\& A=(1)/(2) \int_(\theta_1)^(\theta_2)\left[100 \sin ^2(\theta)-25\right] d \theta\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/xz1887ykmaidx5jlhe7a9y7mgvb00nyto3.png)
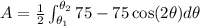
Now, integrate:
![A=(1)/(2)\left[75 \theta-(75)/(2) \sin (2 \theta)\right]_(\theta_1)^(\theta_2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/gvrkzih6akbi5x2dbz4tn8dpy2ytv79fn4.png)
Evaluate at the upper and lower limits:
![A=(1)/(2)\left[(75 \theta_2)/(2)-(75)/(2) \sin \left(2 \theta_2\right)-(75 \theta_1)/(2)+(75)/(2) \sin \left(2 \theta_1\right)\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ruvs6fqemgtbwxte4t2721smn9ishzjtye.png)
Now, use the values
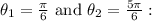
![A=(1)/(2)\left[(75 \pi)/(2)-(75)/(2) \sin \left((5 \pi)/(3)\right)-(75 \pi)/(2)+(75)/(2) \sin \left((\pi)/(3)\right)\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/gzjgp93a7up092s7w5ft9zwxrn1rebqwsj.png)
Simplify the above equation:
![A=(1)/(2)\left[(75 \pi)/(2)+(75 √(3))/(4)-(75 \pi)/(2)+(75 √(3))/(4)\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/896xq93cezmc5n2l87q07szq3zea7mb9y3.png)
Combine like terms: