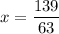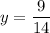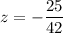Answer:
![\textsf{M}=\left[\begin{array}r-3&0&4&-9\\0&1&-9&6\\0&5&-3&5\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/2wtcntajtw7vfrc7rlm7o65se5rf9geqdt.png)
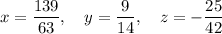
Explanation:
An augmented matrix is formed by combining the matrices with the coefficient terms and the constant terms of a system of linear equations.
System of three linear equations:
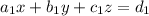
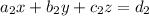
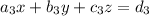
The matrix of coefficients (A) of the three linear equations is:
![\textsf{A}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}a_1&b_1&c_1\\a_2&b_2&c_2\\a_3&b_3&c_3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/iwr4jtz5sfevvcovex24p0rmd8n90gv4sc.png)
The matrix of constant terms (B) of the three linear equations is:
![\textsf{B}=\left[\begin{array}{c}d_1\\d_2\\d_3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/815l484spcmdkyyelxkm4vj76npbuhew9r.png)
The augmented matrix (M) is the combination of the matrices with the coefficient terms and the constant terms:
![\textsf{M} = \left[\begin{array}c\sf A & \sf B\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/mb794jf6cwhp4f7w0826hev8xa1a2k9s5d.png)
![\textsf{M}=\left[\begin{array}ccca_1&b_1&c_1&d_1\\a_2&b_2&c_2&d_2\\a_3&b_3&c_3&d_3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/hf4xk6rdl3n14r2qkhgyezhv2y8t1odbb3.png)

The given system of equations is:
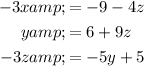
Rearrange each equation so that it is in ax + by + cz = d form:
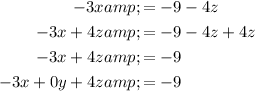
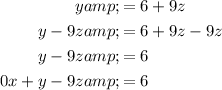
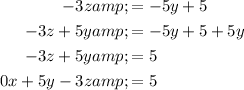
The matrix of coefficients (A) of the three linear equations is:
![\textsf{A}=\left[\begin{array}{rrr}-3&0&4\\0&1&-9\\0&5&-3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/onpprgyzncfro3llv2m308l6m3k6ty5jzm.png)
The matrix of constant terms (B) of the three linear equations is:
![\textsf{B}=\left[\begin{array}{r}-9\\6\\5\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/cggteawrko5etemomoono1u4ddudhv8dgc.png)
Therefore, the augmented matrix (M) is:
![\textsf{M}=\left[\begin{array}rrr-3&0&4&-9\\0&1&-9&6\\0&5&-3&5\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/2wtcntajtw7vfrc7rlm7o65se5rf9geqdt.png)
Each row corresponds to an equation in the system, and the last column contains the constants from the right-hand side of each equation. The columns before the vertical bar represent the coefficients of the variables x, y, and z in the respective equations.
To solve the augmented matrix, use elementary row operations to convert it into the identity matrix
![\left[\begin{array}c1&0&0&p\\0&1&0&q\\0&0&1&r\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/7rusuj5hk3ru4mhql8njf7fw4mo2nfb4or.png)
where the solution to the system will be x = p, y = q, and z = r.
Elementary row operations are:
- Interchange two rows.
- Multiply a row by a constant.
- Add a multiple of a row to another row.
![\textsf{M}=\left[\begin{array}r-3&0&4&-9\\0&1&-9&6\\0&5&-3&5\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/2wtcntajtw7vfrc7rlm7o65se5rf9geqdt.png)
The first step is to get a 1 in the upper left hand corner. To do this, multiply row 1 (R₁) by -1/3:
![\left[\begin{array}r-3&0&4&-9\\0&1&-9&6\\0&5&-3&5\end{array}\right]\begin{array}{c}-(1)/(3)R_1\\\rightarrow\end{array}\left[\begin{array}rrr1&0&-(4)/(3)&3\\0&1&-9&6\\0&5&-3&5\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/3cez3ok28rftjqj052lns9rdw4aj2ajc7i.png)
The next step is to turn the 5 of row 3 (R₃) into a zero. To do this, subtract 5R₂ from R₃:
![\left[\begin{array}rrr1&0&-(4)/(3)&3\\0&1&-9&6\\0&5&-3&5\end{array}\right]\begin{array}{c}R_3-5R_2\\\rightarrow\end{array}\left[\begin{array}rrr1&0&-(4)/(3)&3\\0&1&-9&6\\0&0&42&-25\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/7yb7jpcrlbb670rfllw5ha9xobccix5b21.png)
Now multiply R₃ by 1/42 to turn 42 in R₃ into 1:
![\left[\begin{array}r1&0&-(4)/(3)&3\\0&1&-9&6\\0&0&42&-25\end{array}\right]\begin{array}{c}(1)/(42)R_3\\\rightarrow\end{array}\left[\begin{array}rrr1&0&-(4)/(3)&3\\0&1&-9&6\\0&0&1&-(25)/(42)\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/wpbv6par5ulhnns0h5p790kxzii2e4vmu4.png)
Multiply R₃ by 4/3 and add this to R₁ to turn the -4/3 of R₁ into zero:
![\left[\begin{array}rrr1&0&-(4)/(3)&3\\0&1&-9&6\\0&0&1&-(25)/(42)\end{array}\right]\begin{array}{c}R_1+(4)/(3)R_3\\\rightarrow\end{array}\left[\begin{array}r1&0&0&(139)/(63)\\0&1&-9&6\\0&0&1&-(25)/(42)\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/dtc11i5h00jn69q4uqqu0i26o6ov5wyli5.png)
Multiply R₃ by 9 and add this to R₂ to turn the -9 of R₂ to zero:
![\left[\begin{array}r\vphantom{\frac12}1&0&0&(139)/(63)\\\vphantom{\frac12}0&1&-9&6\\\vphantom{\frac12}0&0&1&-(25)/(42)\end{array}\right]\begin{array}{c}R_2+9R_3\\\rightarrow\end{array}\left[\begin{array}rrr\vphantom{\frac12}1&0&0&(139)/(63)\\\vphantom{\frac12}0&1&0&(9)/(14)\\\vphantom{\frac12}0&0&1&-(25)/(42)\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/9a0xvlfoe13np8hy5p1czkwiobrj3xnrxe.png)
Finally, read off the solutions for x, y and z from the rightmost column: