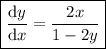Answer:
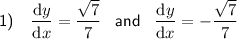
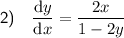
Explanation:
To differentiate an equation that contains a mixture of x and y terms, use implicit differentiation.
Question 1
To differentiate y = 6x²y³ + 2x²y², begin by placing d/dx in front of each term:
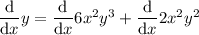
Use the chain rule to differentiate terms in y only.
In practice, this means differentiate with respect to y, and place dy/dx at the end:
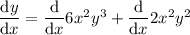
Use the product rule to differentiate the terms in x and y.
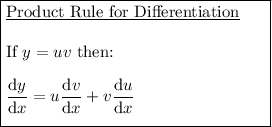

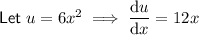
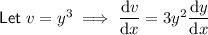
Therefore:
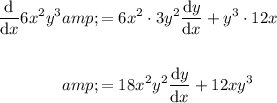

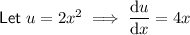
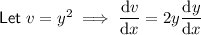
Therefore:
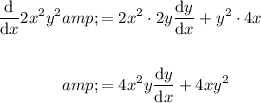
So the final differentiated equation is:
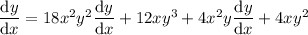
Rearrange the resulting equation to make dy/dx the subject:
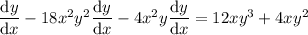
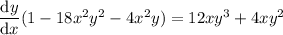
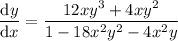
To find dy/dx when x = 1, first find the value of y when x = 1 by substituting x = 1 into the original equation:
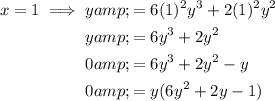
Therefore:
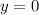
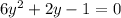
Use the quadratic formula to solve the quadratic:
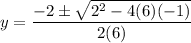
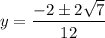

Therefore, the points on the curve y = 6x²y³ + 2x²y² when x = 1 are:
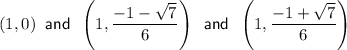
Substitute these points into the differentiated equation:
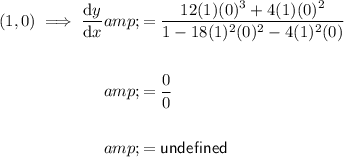
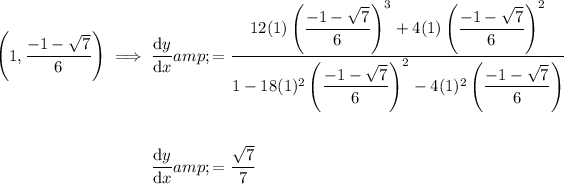
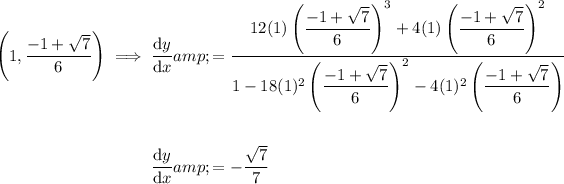
Therefore, dy/dx when y= 6x²y³ + 2x²y² at x = 1 is:
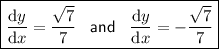

Question 2
To differentiate y = x² +y² - 25, begin by placing d/dx in front of each term:
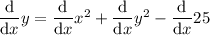
Differentiate the term in x only and the constant term:

Use the chain rule to differentiate terms in y only:
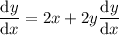
Rearrange the resulting equation to make dy/dx the subject:

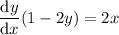
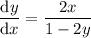
Therefore, dy/dx when y = x² + y² - 25 is: