Question 1:
Final Answer:
- The sales price for a dish with a food cost of $4.55 and a food cost percent of 31% should be $14.68.
- To achieve a food cost percent of 30%, the sales price should be $15.17.
Step-by-step explanation:
- For the first scenario, calculate the sales price using the formula:
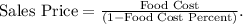
- Substituting values,
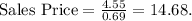
- For the second scenario, determine the sales price for a target food cost percent of 30%:
-
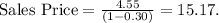
Question 2:
Final Answer:
- Using the overhead-contribution method, the restaurant's food cost percent is 52.95%.
- The restaurant should charge $9.25 for an entrée with a cost per portion of $3.97.
Step-by-step explanation:
- Calculate food cost percent:
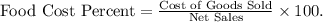
- Substituting values,
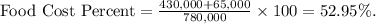
- Determine the sales price for the entrée using the formula:
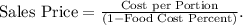
- Substituting values,

Question 3:
Final Answer:
- The sales price for the chicken entrée is $4.48.
Step-by-step explanation:
- Use the prime cost method formula:
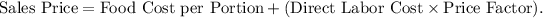
- Substituting values, \
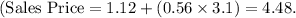
Question 4:
Final Answer:
- The sales price for the appetizer is $5.96.
Step-by-step explanation:
- Apply the actual pricing method formula: {Sales Price} = {Food Cost} + \{Direct Labor Cost} + {Fixed Cost} + {Profit}.
- Substituting values, {Sales Price} = 1.46 + 0.97 + (0.34
 (1.46 + 0.97)) + 0.03 = 5.96 ).
(1.46 + 0.97)) + 0.03 = 5.96 ).
Question 5:
Final Answer:
- The coffee shop should charge $2.39 for a cappuccino.
Step-by-step explanation:
- To achieve a gross profit, use the formula: {Sales Price} = {Cost per Portion} + {Gross Profit per Portion} ).
- Substituting values, {Sales Price} = 0.57 + 1.82 = 2.39 ).
I apologize for the oversight. Let's complete the explanations for the remaining questions.
Question 6:
Final Answer:
- The maximum food cost per sandwich that the chef may have is $1.65.
Step-by-step explanation:
- Calculate the food cost per sandwich using the formula: {Food Cost per Sandwich} = {Menu Price}
 {Food Cost Percent} ).
{Food Cost Percent} ).
- Substituting values, {Food Cost per Sandwich} = 3.99
 0.413 = 1.65 ).
0.413 = 1.65 ).
Question 7:
1. Factors that Impact a Manager's Ability to Charge a Premium:
- Brand reputation and perception.
- Unique selling propositions.
- Economic conditions.
- Market demand and competition.
Question 8:
Final Answer:
- The food cost for the month is $5,882.
Step-by-step explanation:
- Calculate the monthly food cost using the formula: {Food Cost} = {Opening Inventory} + {Purchases} - {Closing Inventory}).
- Substituting values, {Food Cost} = 3,310 + 9,722 - 4,170 = 5,882.
Question 9:
Final Answer:
- The food cost for the business in March is $10,675.
Step-by-step explanation:
- Calculate the food cost by considering opening inventory, purchases, employee meals, promotions, and steward sales: {Food Cost} = \{Opening Inventory} + {Purchases} - {Closing Inventory} + {Employee Meals} + {Promotions} - {Steward Sales}).
- Substituting values, {Food Cost} = 378 + 12,706 - 144 + 588 + 831 - 701 = 10,675.
Question 10:
Final Answer:
- The restaurant's food cost percent is 31.6%, and the variance from the standard is within an acceptable range.
Step-by-step explanation:
- Calculate the food cost percent:
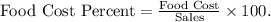
- Substituting values,
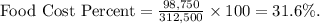
- The variance from the standard is within + or - 0.5%, indicating acceptable performance.
Question 11:
1. Possible Problems Causing a Higher Food Cost Percent:
- Wastage and spoilage.
- Theft or pilferage.
- Inefficient portion control.
2. Possible Problems Causing a Lower Food Cost Percent:
- Quality compromise in ingredients.
- Incorrect inventory valuation.
Question 12:
1. Identification of the Problem:
- With a POS system, the manager can track sales anomalies, voids, or excessive discounts associated with the server's transactions.
2. Identification without a POS System:
- Without a POS system, the manager may need to rely on surveillance footage, witness statements, or irregularities in cash handling to identify discrepancies. Implementing tighter inventory control measures can also help uncover potential issues.