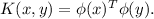Final Answer:
![\[ \phi(x) = \begin{bmatrix} x_1^2 \\ √(2)x_1x_2 \\ x_2^2 \\ √(2)x_1 \\ √(2)x_2 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/computers-and-technology/college/ifywotlt00nvql6rk8p5z6mtysw7hq5pf5.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
The 3rd-order polynomial kernel can be expressed as:
![\[ K(x, y) = (x^T y + 1)^3 \].](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/computers-and-technology/college/y4l5upknfpwop6z7b8k3le2lmm4jokv5pc.png)
To find the explicit mapping \(\phi\), we can use the binomial expansion:
![\[ (a+b)^3 = a^3 + 3a^2b + 3ab^2 + b^3 \].](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/computers-and-technology/college/3k7eu7ewmdd45svmxrzkrfge4kr8vnajet.png)
For our kernel,
 and
and
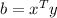 . Expanding, we get:
. Expanding, we get:
![\[ K(x, y) = (1 + x^T y)^3 = 1 + 3(x^T y) + 3(x^T y)^2 + (x^T y)^3 \].](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/computers-and-technology/college/wr8j9s0tn6budjz0wezoh9ayg0ivzcwl8j.png)
Now, express this in terms of the feature vector
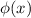 :
:
![\[ \phi(x)^T \phi(y) = 1 + √(3)x_1y_1 + 3x_1x_2y_1y_2 + √(3)x_2y_2 + (x^T y)^3 \].](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/computers-and-technology/college/n75oauxhvws76stvzv2n6doy25e7suuxnh.png)
Comparing coefficients, we find
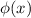 :
:
![\[ \phi(x) = \begin{bmatrix} x_1^2 \\ √(2)x_1x_2 \\ x_2^2 \\ √(2)x_1 \\ √(2)x_2 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \].](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/computers-and-technology/college/efq1n4u8tau7yoqbb20tj5ztabkhjku5rg.png)
This mapping
 allows us to compute the inner product efficiently as
allows us to compute the inner product efficiently as