Answer:
Osmolarity is approximately 0.278 moles/L.
Step-by-step explanation:
Osmolarity is a measure of the concentration of solute particles in a solution. It is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. Osmolarity is important in biology because it affects the movement of water across cell membranes.
For The Question:
Given:
- Concentration of glucose solution = 5.0% (m/v) glucose
- Molar mass of glucose (C6H12O6) = 180 g/mol
Let's calculate the mass of glucose in the solution.
For a 100 mL solution (which is a typical volume used for calculations):
5.0% of 100 mL =
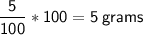
Converting the mass of glucose to moles.

Substituting Value,
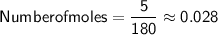
Now,
Calculating the osmolarity.
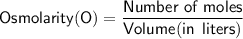
Since the volume is given in milliliters, we need to convert it to liters:
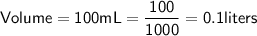
Now,
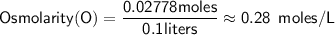
Therefore, the osmolarity of the 5.0% (m/v) glucose solution is approximately 0.278 moles/L.