Answer:
B) 35.5 N at an angle 34.3° with respect to the +x-axis.
Step-by-step explanation:
Rewrite each force in component form (where vectors are represented using the unit vectors i and j along the x and y axes):
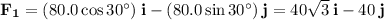
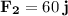
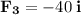
Resolve the forces:
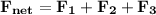
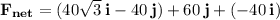
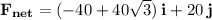
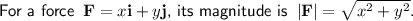
Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force:
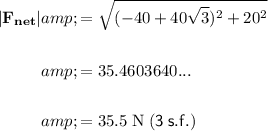
The direction θ can be found by finding the angle with the horizontal, which is given by:
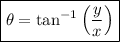
Note that tan⁻¹(y/x) will be the direction θ when 0 < θ < 90°.
When θ is between 90° and 360°, we may need to add or subtract this angle to/from 180° or 360°.
The values of x and y are:
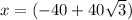
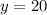
As both values are positive, the resultant vector lies in quadrant I, so we can simply calculate θ (without the need to add or subtract the angle to or from 180° or 360°).
Therefore:
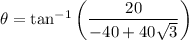
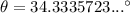
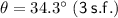
Therefore, the resultant (net) vector force acting on the particle O is given by 35.5 N at an angle 34.3° with respect to the +x-axis.