To find the pH of a solution, we use a formula that relates pH to the hydrogen ion concentration. The pH measures how acidic or basic a solution is. When the pH is less than 7, the solution is acidic, when it is greater than 7, the solution is basic (alkaline), and a pH of 7 indicates neutrality. Now, let's calculate the pH of pure water, where the hydrogen ion concentration ([H+]) is 10^-7 moles per liter.
![pH=-log[H+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/9hox30mi4zmttu9gmh6wymeen97kwczmjs.png)
ph = potential of hydrogen
H+ = concentration of hydrogen ions
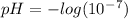
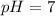
Answer: The pH of the pure water is 7.