Answer: D: 1/3

Step-by-step explanation:
The question mentioned that the increase in velocity is uniform, which means that the acceleration is constant. (Since a = dv/dt, which means that acceleration is the rate of change for velocity.)
For better view, if we establish a function for velocity in terms of t,
v(t) = at + 1
as its derivative must be constant a in which its initial velocity was 1m/s.
Substituting t at each occasion,
at t = 0, v = 1 (m/s)
at t = 6, v = 6a + 1 (m/s)
in which after 6 seconds where the velocity started to uniformly increase, the velocity of the fish was 3m/s.
Therefore,
at t = 6,
v = 6a + 1 = 3.
Subtracting 1 in each side,
6a = 2,
Dividing 6 to each side,
a = 1/3 (m/s^2)
And our final answer is D: 1/3 (m/s^2)
If you just want to solve the question in simple method whenever you see a question like this,
ONLY when given that the increase in velocity is uniform,
you can just subtract initial velocity from the final velocity and divide it by time taken.
Like this:
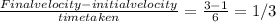 (m/s^2)
(m/s^2)
*Please note that the unit for acceleration is
 as it is the rate of change for velocity(m/s)
as it is the rate of change for velocity(m/s)