Charles' Law is a law demonstrating the relationship between temperature and volume of a gas. It states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature at a constant pressure. It is represented by the equation
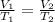 , where
, where
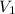 and
and
 represent the initial conditions while
represent the initial conditions while
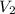 and
and
 represent the final conditions. It's important to note that the units for temperature must be in Kelvin.
represent the final conditions. It's important to note that the units for temperature must be in Kelvin.
An example of Charles' law being observed in our daily lives is in the process of baking. Yeast is a common ingredient used to make dough rise through the release of carbon dioxide bubbles. The increase in temperature during baking causes the carbon dioxide gas to expand further inside the dough, which in turn makes the dough rise.