- To solve this answer, first convert the masses of the two elements into moles. You can do this by using their molar masses, which can be found on the periodic table.
The molar mass of Helium is 4.00g
3.38g ×
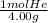 = 0.845 mol He
= 0.845 mol He
The molar mass of Neon is 20.18g
2.21g ×
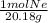 = 0.10951 mol Ne
= 0.10951 mol Ne
- Next, use the ideal gas law equation [PV=nRt] to find the individual pressures of both elements. *You can rewrite this equation to
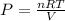 to isolate P*
to isolate P*
P= pressure [?] n= moles [0.845 mol He, 0.10951 mol Ne]
V= volume [2.36L] R= gas constant [0.0821]
T= temperature [25+273.15= 298.15 K]
Plug in your values to find the pressure of Helium and the pressure of Neon. After doing this process twice you should end up with the Helium's pressure of 8.76 atm and Neon's pressure of 1.14 atm. These are the partial pressures.
To find the total pressure in the container, add 1.14 and 8.76, which equals 9.9 atm.