Answer:
12 hours
Explanation:
To write an equation that best models the given data, we can plot the points on a coordinate graph, where the months are along the x-axis and the number of daylight hours are along the y-axis. Let x = 1 be January, x = 2 be February, and so on.
After plotting the points on the graph, we can see that the shape of the graph is sinusoidal.
Using the sinusoidal regression function of a graphical calculator to find a trigonometric model that gives the curve of best fit, we get:
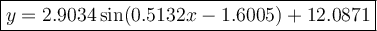
(where the argument of the sin function is measured in radians, and each coefficient is rounded to 4 decimal places).
As the graph is periodic, the expected average number of daylight hours in March 2023 will be the same as the expected average number of daylight hours in March of any year.
As the sinusoidal regression curve is very close to all points on the graph, we would expect the average number of daylight hours to be the same as (or very close to) the values given in the table, i.e. 12 hours.
As the month of March is represented by x = 3, substitute x = 3 into the equation to calculate the expected average number of daylight hours in March 2023:
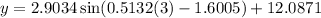
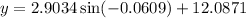
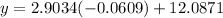
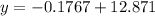
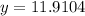
The expected average number of daylight hours in March 2023 rounded to the nearest quarter-hour is 12 hours, which is the same as the recorded average number of daylight hours in March 2015.