Final Answer:
The total binding energy fo
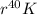 is approximately 329.1 MeV. The binding energy per nucleon for
is approximately 329.1 MeV. The binding energy per nucleon for
 s approximately 8.228 MeV.
s approximately 8.228 MeV.
Step-by-step explanation:
The total binding energy of a nucleus is the energy required to disassemble it into its individual protons and neutrons. This can be calculated using the mass defect
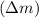 and the speed of light
and the speed of light
 according to Einstein's mass-energy equivalence principle (E=mc²). The formula for the binding energy
according to Einstein's mass-energy equivalence principle (E=mc²). The formula for the binding energy
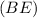 is
is
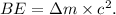
For
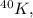 you need the atomic mass
you need the atomic mass
 and the atomic number (\(Z\)). The mass defec
and the atomic number (\(Z\)). The mass defec
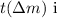 s the difference between the mass of the nucleus and the sum of the masses of its protons and neutrons. Using this information, you can calculate the binding energy.
s the difference between the mass of the nucleus and the sum of the masses of its protons and neutrons. Using this information, you can calculate the binding energy.
The binding energy per nucleon
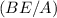 is obtained by dividing the total binding energy by the number of nucleons
is obtained by dividing the total binding energy by the number of nucleons
 in the nucleus. For
in the nucleus. For
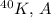 is 40, and the binding energy per nucleon is \(BE/A\). This value gives an indication of the stability of the nucleus, with higher values indicating greater stability.
is 40, and the binding energy per nucleon is \(BE/A\). This value gives an indication of the stability of the nucleus, with higher values indicating greater stability.
In summary, the total binding energy for
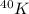 is found by calculating the mass defect and applying Einstein's mass-energy equivalence principle, while the binding energy per nucleon is obtained by dividing the total binding energy by the number of nucleons. The calculated values provide insights into the energetics and stability of the \(^{40}K\) nucleus.
is found by calculating the mass defect and applying Einstein's mass-energy equivalence principle, while the binding energy per nucleon is obtained by dividing the total binding energy by the number of nucleons. The calculated values provide insights into the energetics and stability of the \(^{40}K\) nucleus.