Answer:
d. 41 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
To find the pressure exerted by the gas, we need to use the ideal gas law. The ideal gas law is an equation in thermodynamics that describes the behavior of a hypothetical ideal gas and relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of the gas. It is expressed by the equation PV = nRT, where P is the pressure in atm, V is the volume in liters, n is the number of moles, R is the universal gas constant in L·atm / (K·mol), and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
We can rearrange the equation to solve for pressure.
- PV = nRT
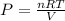
Now, plug in the values with the appropriate units.
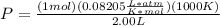
- P = 41.025 atm
The pressure exerted by one mole of an ideal gas contained in a 2.00 L container at 1000 K is d. 41 atm.