Final Answer:
The root mean square (rms) speed of an oxygen gas molecule (O2) at 21.0 °C is approximately 484 meters per second.
Step-by-step explanation:
The root mean square speed of gas molecules can be calculated using the formula
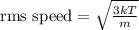 , where
, where
 is the Boltzmann constant,
is the Boltzmann constant,
 is the temperature in Kelvin, and
is the temperature in Kelvin, and
 is the mass of the molecule. For an oxygen molecule
is the mass of the molecule. For an oxygen molecule
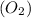 , the molar mass
, the molar mass
 is approximately 32 grams/mol. Converting this to kilograms
is approximately 32 grams/mol. Converting this to kilograms
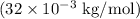 and plugging in the values into the formula, we find the rms speed.
and plugging in the values into the formula, we find the rms speed.
At 21.0 °C, the temperature in Kelvin
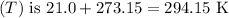 . Substituting the values into the formula:
. Substituting the values into the formula:
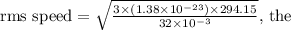 calculation yields an rms speed of approximately 484 m/s.
calculation yields an rms speed of approximately 484 m/s.
In summary, the root mean square speed of an oxygen gas molecule at 21.0 °C is approximately 484 meters per second.