Answer:
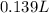
Step-by-step explanation:
To dilute the potassium iodide solution
--->
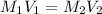
where
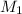 is the initial concentration of the solution,
is the initial concentration of the solution,
 is the initial volume of the solution,
is the initial volume of the solution,
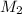 is the final concentration of the solution, and
is the final concentration of the solution, and
 is the final volume of the solution.
is the final volume of the solution.
We can rearrange this formula to solve for
 :
:
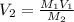
Substituting the given values, we get:
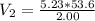
- Note that we need to convert the initial volume from milliliters to liters to ensure consistent units in the calculation.
53.6 mL is equal to 0.0536 L.
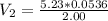
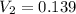
Therefore, the final volume of the solution is 0.139 L.