Your friend is offering to pay you an annuity of $4,000 at the end of each year for 5 years. To determine if this offer is a good deal.
To calculate the present value of the annuity, we need to discount each payment to its present value. We can use the formula for the present value of an ordinary annuity:
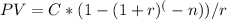
Where PV is the present value, C is the cash flow (annuity payment), r is the interest rate, and n is the number of periods.
Let's plug in the values:
PV = $4,000 * (1 - (1 + 0.025)^(-5)) / 0.025
Simplifying the equation:
PV = $4,000 * (1 - 1.025^(-5)) / 0.025
FV = PV * (1 + r)^n
FV = $18,422.35 * (1 + 0.025)^5
In summary, accepting your friend's offer of $18,422.35 in cash today in exchange for the annuity payments would be a better financial decision compared to earning 2.5% on your money in other investments with equal risk.