Let f(1) =
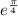 , f'(1) = 5
, f'(1) = 5
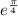 , g(1) = -3, and g'(1) = 1, find h'(1), where h(x) = g(x)arctan(ln(f(x))). So, h'(1) = 0.396
, g(1) = -3, and g'(1) = 1, find h'(1), where h(x) = g(x)arctan(ln(f(x))). So, h'(1) = 0.396
Let f(1) =
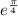 , f'(1) = 5
, f'(1) = 5
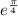 , g(1) = -3, and g'(1) = 1.
, g(1) = -3, and g'(1) = 1.
To find h'(1), where h(x) = g(x)arctan(ln(f(x))), we proceed as follows
To find h'(x), since h(x) = g(x)arctan(ln(f(x))), we need to find h'(x). using the product rule of differentiation
duv/dx = uv' + vu'
Now, u = g(x) and v = arctan(ln(f(x)))
Let ln(f(x)) = w
Differentiating, we have
u'(x) = g'(x) and
v'(x) = (arctan(w))' = (arctan(w))/dw × dw/df × df(x)/dx = 1/[1 + w²] × 1/f(x) × f'(x)
= 1/[1 + (ln(f(x))²] × 1/f(x) × f'(x)
= f'(x)/{[1 + (ln(f(x))²]f(x)}
h'(x) = uv' + vu'
So, substituting the values of the variables into the equation, we have that
= g(x)f'(x)/{[1 + (ln(f(x))²]f(x)} + arctan(ln(f(x)))(g'(x))
Since x = 1
h'(1) = g(1)f'(1)/{[1 + (ln(f(1))²]f(1)} + arctan(ln(f(1)))(g'(1))
Given that
- f(1) =
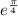 ,
, - f'(1) = 5
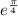 ,
, - g(1) = -3, and
- g'(1) = 1.
Substituting the values of the variables into the equation, we have that
h'(1) = g(1)f'(1)/{[1 + (ln(f(1))²]f(1)} + arctan(ln(f(1)))(g'(1))
h'(1) = (-3)
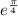 ,/{[1 + (ln(5
,/{[1 + (ln(5
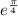 )²]e^(π/4)} + arctan(ln(
)²]e^(π/4)} + arctan(ln(
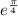 )(1)
)(1)
h'(1) = -3/{[1 + (ln(5
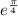 )²]} + arctan(ln(
)²]} + arctan(ln(
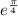 )(1)
)(1)
h'(1) = -3/{[1 + (ln(5
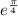 )²]} + arctan(π/4ln(e))
)²]} + arctan(π/4ln(e))
h'(1) = -3/{[1 + (ln5 + ln
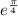 )²]} + arctan(π/4 × 1)
)²]} + arctan(π/4 × 1)
h'(1) = -3/{[1 + (ln5 + π/4 × lne)²]} + arctan(π/4 × 1)
h'(1) = -3/{[1 + (ln5 + π/4 × 1)²]} + arctan(π/4)
h'(1) = -3/(1 + (ln5 + π/2)²)+ arctan(π/4)
h'(1) = -3/[1 + (1.6094 + π/2)²]+ arctan(0.7854)
h'(1) = -3/(1 + (1.6094 + 1.5708)² + 0.6658
h'(1) = -3/(1 + 3.1802²) + 0.6658
h'(1) = -3/(1 + 10.1137) + 0.6658
h'(1) = -3/11.1137 + 0.6658
h'(1) = -0.2699 + 0.6658
h'(1) = 0.3959
h'(1) ≅ 0.396