Answer:
pH = 9.217
Step-by-step explanation:
When water undergoes self dissociation, since it is an amphiprotic solvent:
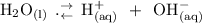
From the dissociation constant (hydrolysis constant, Kh):
![{ \rm{k _(h) = \frac{[H {}^( + ) ][OH {}^( - ) ] }{[H _(2) O]} }} \\](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/tjz4c0xtiebi2168g453m2ywsod9v5d6kw.png)
But activity of water is 1, so [H2O] = 1
![{ \rm{k _(h) = {[H {}^( + ) ][OH {}^( - ) ]}}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/wlf8xn339niv4irm1qbihf09hrcrwwyemc.png)
But Kh = 1 × 10^-14, and [OH-] = 1.65 × 10^-5
![\rm{(1 * {10}^( - 14) ) = {[H {}^( + ) ] * (1.65 * {10}^( - 5)) }} \\ \\ { \rm{{[H {}^( + ) ]}}}{ \rm{ = 6.06x {10}^( - 10) }}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/gs9efo9qsz1rzdoyc0yhg1jwrwb9g22me1.png)
From the formula of pH;
![{ \rm{p{H = - log {[H {}^( + ) ]}}}} \\ { \rm{p{H }} = - log(6.06 * {10}^( - 10) ) } \\ \\ { \underline{ \rm{ \: pH = 9.217 \: }}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/sbsgdkmho8aqoypie81bz6op55hzv4qu4z.png)