The
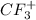 ion has a central carbon atom with three fluorine atoms bonded to it and one positive charge indicating a missing electron. In terms of electron geometry (eg), the carbon atom originally has four areas of electron density (three from the fluorine atoms and one from the lone pair).
ion has a central carbon atom with three fluorine atoms bonded to it and one positive charge indicating a missing electron. In terms of electron geometry (eg), the carbon atom originally has four areas of electron density (three from the fluorine atoms and one from the lone pair).
However, when it loses an electron and becomes positively charged, it has only three areas of electron density, which makes the geometry trigonal planar.
Since there is no lone pair on the carbon atom in the
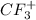 ion, the molecular geometry (mg) is the same as the electron geometry, which is also trigonal planar.
ion, the molecular geometry (mg) is the same as the electron geometry, which is also trigonal planar.
To show the Lewis structure for
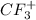 , you would draw the carbon in the center with three fluorine atoms around it, each bonded to the carbon with a single line representing a pair of shared electrons.
, you would draw the carbon in the center with three fluorine atoms around it, each bonded to the carbon with a single line representing a pair of shared electrons.
Each fluorine will have three pairs of dots representing the remaining six electrons that are not involved in bonding. The carbon will not have any lone pairs of electrons, indicating that it has given up one electron, hence the positive charge.