To write a complete ionic equation, I would first separate each of the elements and their respective charges, subscripts, and coefficients.
For CaBr2(aq):
Ca has a 2+ charge and a coefficient of 1. Ca+
Br has a charge of -1 and has a subscript of 2. Br-
For 2AuClO4(aq):
Au has a charge of 1+ because perchlorate (ClO4) has a charge of -1, so they must be "cancel" in charges in order to form. Au also has a coefficient of two. 2Au+
ClO4 has a charge of -1 and has a coefficient of 2. 2ClO4-
For 2AuBr(s):
You can leave this alone in the complete ionic equation since it is a solid precipitate of the reaction and has little to no ions dissociating.
For Ca(ClO4)2(aq):
Ca has a charge of 2+ and a coefficient of 1. Ca2+
ClO4 has a charge of 1-, a coefficient of one, but also a subscript of 2. 2ClO4-
Thus, when separating and combining everything, you should be left with:
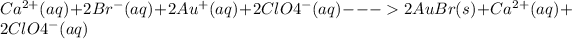
Hope this helps!