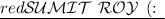To determine the change in volume (V) given the changes in pressure (P) and temperature (T), we need to consider the relationship described by the ideal gas law:
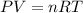
Where:
- - P is the pressure
- - V is the volume
- - n is the number of moles of gas
- - R is the ideal gas constant
- - T is the temperature
To analyze the effect of changing P and T on V, we'll assume that the number of moles (n) and the ideal gas constant (R) remain constant.
If P increases by a factor of 5, we can express the new pressure as:
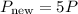
If T decreases by a factor of 3, we can express the new temperature as:
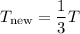
Now, let's consider the relationship between the initial and final volumes (V and V_new):
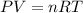
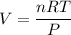
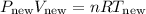
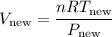
Substituting the expressions for P_new and T_new, we have:
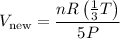
Simplifying the expression:
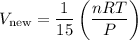
Comparing this with the initial volume (V), we can see that:
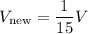
Therefore, the change in volume (V) is such that it decreases by a factor of 15.
The correct option is E. V decreases by a factor of 15.
♥️