Answer & Explanation:
To solve this problem, we need to set the gravitational force acting on the bead equal to the electric force acting on it. The bead will hang suspended in the air when these two forces are equal.
The gravitational force
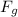 is given by:
is given by:
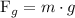
where
 is the mass of the bead and
is the mass of the bead and
 is the acceleration due to gravity.
is the acceleration due to gravity.
The electric force
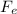 is given by:
is given by:
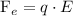
where
 is the charge of the bead and
is the charge of the bead and
 is the electric field strength.
is the electric field strength.
Setting these two equal gives:
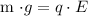
Solving for
 gives:
gives:
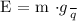
Given that the mass
 of the bead is 0.10 g (or 0.10/1000 kg), the acceleration due to gravity
of the bead is 0.10 g (or 0.10/1000 kg), the acceleration due to gravity
 is approximately 9.8 m/s², and the charge
is approximately 9.8 m/s², and the charge
 is the charge of
is the charge of
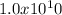 electrons (with the charge of one electron being approximately
electrons (with the charge of one electron being approximately
 , we can substitute these values into the formula to find the electric field strength. Let's calculate that.
, we can substitute these values into the formula to find the electric field strength. Let's calculate that.
The electric field strength that will cause the bead to hang suspended in the air is approximately
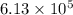 N/C (Newtons per Coulomb).
N/C (Newtons per Coulomb).