Answer:
Capacitors are devices that store (electrical)energy. They usually consist of an insulating material inserted between two conductive plates. When a voltage is applied across the plates, electric charge builds up on the plates. The ratio of charge on one plate to the voltage across the plates is called the capacitance. The SI unit for capacitance is the farad (F).
Additional Information:
What is a capacitor?
A capacitor is an electronic device that stores electrical energy. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. When a voltage is applied across the plates, one plate accumulates a positive charge while the other plate accumulates an equal and opposite negative charge. This charge separation creates an electric field between the plates.
The capacitance of a capacitor, denoted by the symbol "C," determines its ability to store charge. It is defined as the ratio of the magnitude of charge stored on one plate (Q) to the potential difference (V) across the plates: C = Q/V. The unit of capacitance is the farad, F.
Capacitors store electrical energy in the electric field created between the plates. The amount of energy stored in a capacitor is given by the equations:
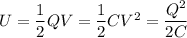
Where:
- "U" represents the stored energy
- "V" is the voltage across the capacitor
- "Q" is the charge stored in the capacitor
- "C" is the capacitance