Answer:
The electrostatic force is a vector quantity, which means that it has both magnitude and direction. Coulomb's law tells you the the magnitude of the electrostatic force. To determine the direction of the force, you can draw a diagram using force vectors.
Additional Information:
What is Coulomb's law?
Coulomb's law states that the magnitude of the electrostatic force between two charged objects is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Mathematically, Coulomb's law is expressed as:
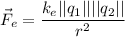
Where:
- "F_e" represents the magnitude of the electrostatic force between the two charges.
- "k_e" is the electrostatic (aka Coulomb's constant) constant (k ≈ 8.99 x 10^9 N m^2/C^2).
- "q_1" and "q_2" are the magnitudes of the charges of the two objects.
- "r" is the distance between the centers of the charged objects.
Coulomb's law helps quantify the strength of the electrostatic force and provides a mathematical relationship to calculate the force between charged objects based on their charges and distance.

What is a vector?
A vector is a mathematical object that has both magnitude and direction. It is used to represent physical quantities that require both of these components to be fully described, such as displacement, velocity, force (in this case it's the electrostatic force), and acceleration.
In a vector, the magnitude represents the size or length of the vector, while the direction indicates the orientation or angle of the vector in space. Vectors are typically represented by arrows, where the length of the arrow corresponds to the magnitude, and the direction of the arrow indicates the direction of the vector.

How do we find the direction a net electrostatic force exerts?
To determine the direction of an electrostatic force between charged objects, you need to consider the following principles:
- Like charges repel: If the charges on the objects have the same sign (both positive or both negative), they will exert repulsive forces on each other. The direction of the force will be away from each charge.
- Unlike charges attract: If the charges on the objects have opposite signs (one positive and one negative), they will exert attractive forces on each other. The direction of the force will be towards the charge with the opposite sign.
- Superposition principle: If there are multiple charges involved, you need to consider the vector sum of the individual forces exerted by each charge. This means adding the forces as vectors to find the resultant force and its direction.
In general, you can determine the direction of the electrostatic force by considering the signs of the charges and applying the principles of attraction and repulsion.
**Noting what I said in principle #3: I like to use a different form of Coulomb's Law when dealing with multiple charges. Although I won't get in too much detail about this, as I am assuming you are just learning about electrostatic physics.