The force exerted by Block A on Block B is 2.0 Newtons.
To calculate the force exerted by Block A on Block B, you can use Newton's third law of motion, which states that action and reaction forces are equal and opposite.
Given:
Force applied on Block A (F) = 3.0 N (applied force)
Mass of Block A
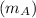 = 5.0 kg
= 5.0 kg
Mass of Block B
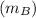 = 10 kg
= 10 kg
The force exerted by Block A on Block B is the same as the force that causes both blocks to move together.
Acceleration of the system:
![\[ \text{Acceleration} = \frac{\text{Net Force}}{\text{Total Mass}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/tssi8dev52frhdhmg93umknb6muhqtdu8u.png)
The net force acting on the system is the force applied to Block A:
![\[ \text{Net Force} = F = 3.0 \, \text{N} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/m5vrrdbs3isz41qw500ik7v5qej5nipb43.png)
Total mass of the system:
![\[ \text{Total Mass} = m_A + m_B = 5.0 \, \text{kg} + 10 \, \text{kg} = 15.0 \, \text{kg} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/dzdd4dtbw6botlsoe4nog78eukj14ltx88.png)
Now, calculate the acceleration:
![\[ \text{Acceleration} = \frac{F}{\text{Total Mass}} = \frac{3.0 \, \text{N}}{15.0 \, \text{kg}} = 0.2 \, \text{m/s}^2 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/ubt7lbpgcq3osvlbxfox1l9ec8wj15fu6f.png)
Since the blocks move together, the force exerted by Block A on Block B can also be found using Newton's second law:
![\[ \text{Force} = \text{mass} * \text{acceleration} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/6pi5zd5em3bfujrlhlyk0q88bihzhjkfwd.png)
![\[ \text{Force} = m_B * \text{Acceleration} = 10 \, \text{kg} * 0.2 \, \text{m/s}^2 = 2.0 \, \text{N} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/mqi4h3069vl0t33ez8ec399floaaps3m8i.png)