Determine the [OH^-], pH, and pOH of a solution with a [H^+] of 4.9×10^-13 M at 25 °C.
Given:
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)] = 4.9 * 10^(-13) \, M](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/bpr8oollxvgouunf30xd2tiukta2hbksw1.png)
To find [OH^-], we can use the equation for the ion product of water:
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)][OH^(-)] = 1.0 * 10^(-14)](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/h7l3wy3x6y8rob9tw5w3jbvv8pdc24ba6k.png)
Since we know [H^+], we can rearrange the equation to solve for [OH^-]:
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)] = (1.0 * 10^(-14))/([H^(+)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/zz741o4g5u27gwsgveeqdv1mlmhep9u1ts.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)] = (1.0 * 10^(-14))/(4.9 * 10^(-13))](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/nt6oiwmydz58ogxh3nc7iny519751kj2iz.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)] \approx 2.04 * 10^(-2) \, M](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/6g0uuntbfyukn0gphy0jdhbrokdmdjyj8h.png)
To find the pH, we can use the equation:
![\displaystyle\sf pH = -\log[H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/4o182clsxlbukotglsz4in2pwt589jr6hl.png)
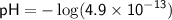
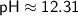
To find the pOH, we can use the equation:
![\displaystyle\sf pOH = -\log[OH^(-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/yx8r2p4incwowex399x8r7lghj1d4gnptj.png)
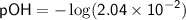
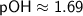
Therefore, in the given solution, [OH^-] ≈ 2.04×10^-2 M, pH ≈ 12.31, and pOH ≈ 1.69.
-------------------
Determine the [H^+], pH, and pOH of a solution with an [OH^-] of 8.8×10^-13 M at 25 °C.
Given:
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)] = 8.8 * 10^(-13) \, M](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ji8x14d6x9argcoc7mpcozol9d1qm1mb6z.png)
Using the ion product of water equation, we can find [H^+]:
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)][OH^(-)] = 1.0 * 10^(-14)](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/h7l3wy3x6y8rob9tw5w3jbvv8pdc24ba6k.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)] = (1.0 * 10^(-14))/([OH^(-)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/1435nt3di7774kuole02pkrrgolso8hszw.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)] = (1.0 * 10^(-14))/(8.8 * 10^(-13))](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/swhlftizuurfea66fq30nbpi9qtxfiy3e6.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)] \approx 1.14 * 10^(-2) \, M](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/8h42wvtjfa371lwhfhuvqgu7es2xqaizqi.png)
To find the pH, we can use the equation:
![\displaystyle\sf pH = -\log[H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/4o182clsxlbukotglsz4in2pwt589jr6hl.png)
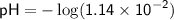
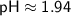
To find the pOH, we can use the equation:
![\displaystyle\sf pOH = -\log[OH^(-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/yx8r2p4incwowex399x8r7lghj1d4gnptj.png)
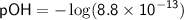
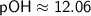
Therefore, in the given solution, [H^+] ≈ 1.14×10^-2 M, pH ≈ 1.94, and pOH ≈ 12.06.
-------------------
Determine the |H^+|, |OH^-|, and pOH of a solution with a pH of 3.72 at 25 °C.
Given:

To find [H^+], we can use the equation:
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)] = 10^(-pH)](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/c83bf5vfbd6sokravuzwasxejcw8drako2.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)] = 10^(-3.72)](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/o41834xipcv2pfr5jdz8rptp8kmi15me34.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)] \approx 2.2 * 10^(-4) \, M](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/19e1a51sjncp4xhpf2qic3zk22e2061xw0.png)
Since water is neutral, [H^+][OH^-] = 1.0×10^-14. Therefore, we can find [OH^-]:
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)] = (1.0 * 10^(-14))/([H^(+)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/zz741o4g5u27gwsgveeqdv1mlmhep9u1ts.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)] = (1.0 * 10^(-14))/(2.2 * 10^(-4))](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ii1zq2ltp9cnzxamlyluiw9d16wq6ry23h.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)] \approx 4.55 * 10^(-11) \, M](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/6wvuzdjattismeg8usgl6rq3t8qwptp744.png)
To find the pOH, we can use the equation:
![\displaystyle\sf pOH = -\log[OH^(-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/yx8r2p4incwowex399x8r7lghj1d4gnptj.png)
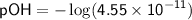
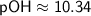
Therefore, in the given solution, |H^+| ≈ 2.2×10^(-4) M, |OH^-| ≈ 4.55×10^(-11) M, and pOH ≈ 10.34.
-------------------
Determine the [H^+], [OH^-], and pH of a solution with a pOH of 9.45 at 25 °C.
Given:
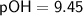
To find [OH^-], we can use the equation:
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)] = 10^(-pOH)](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/mtjqsz2yot7irg7png22a9cb23s9td6vro.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)] = 10^(-9.45)](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/gajj88qs6dbch51ze8273ucczns0m2ntgw.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)] \approx 3.52 * 10^(-10) \, M](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/y5euk28hv7rc3gw0ww0g7on16zdxqfu1v8.png)
Since water is neutral, [H^+][OH^-] = 1.0×10^-14. Therefore, we can find [H^+]:
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)] = (1.0 * 10^(-14))/([OH^(-)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/1435nt3di7774kuole02pkrrgolso8hszw.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)] = (1.0 * 10^(-14))/(3.52 * 10^(-10))](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/36d684d7wykiswegltofbnkipdap1gaw3v.png)
![\displaystyle\sf [H^(+)] \approx 2.84 * 10^(-5) \, M](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/opwegb67eyv4d1nuwr2u5quq70s3mp9pml.png)
To find the pH, we can use the equation:
![\displaystyle\sf pH = -\log[H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/4o182clsxlbukotglsz4in2pwt589jr6hl.png)
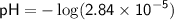
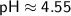
Therefore, in the given solution, [H^+] ≈ 2.84×10^-5 M, [OH^-] ≈ 3.52×10^-10 M, and pH ≈ 4.55.