So, the amplitude
 is
is
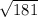 and the phase angle
and the phase angle
 is given by the arctangent of the ratio of the coefficients of the sine and cosine terms.
is given by the arctangent of the ratio of the coefficients of the sine and cosine terms.
Let's express the given current in the form
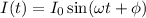 and find the amplitude
and find the amplitude
 and the phase angle
and the phase angle
 .
.
Given current:
![\[ I(t) = 8 \sin(\omega t) + 6 \cos(5 \omega t - 120^\circ) \, \text{A} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/b6wd93a2hb14hdpnopcr31t35wja1g3xl1.png)
Let's use trigonometric identities to rewrite the current expression in the desired form:
![\[ I(t) = I_0 \sin(\omega t + \phi) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/91j5kiihqi0zcw9rig4io3nbtgza4569l4.png)
Comparing coefficients, we have:
1. For the term
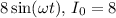 , and there is no phase shift
, and there is no phase shift
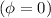 .
.
2. For the term
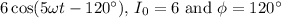 .
.
So, the current expression becomes:
![\[ I(t) = 8 \sin(\omega t) + 6 \cos(5 \omega t - 120^\circ) \]\[ I(t) = 8 \sin(\omega t) + 6 \cos(5 \omega t - 120^\circ) \]\[ I(t) = 8 \sin(\omega t) + 6 \cos(5 \omega t) \cdot \cos(120^\circ) - 6 \sin(5 \omega t) \cdot \sin(120^\circ) \]\[ I(t) = 8 \sin(\omega t) - 3 \cos(5 \omega t) - 6 √(3) \sin(5 \omega t) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/um0hnt9pn58usgiqxbbwkljv9flnrld4jm.png)
Now, let's combine the sine and cosine terms:
![\[ I(t) = A \sin(\omega t + \phi) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/rb3zpq14tmjqors0qttq3o8wnu9bt2ai6k.png)
Where:
![\[ A = \sqrt{8^2 + (-3)^2 + (-6√(3))^2} = √(64 + 9 + 108) = √(181) \]\[ \phi = \arctan\left((-6√(3))/(8)\right) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/tqtelm47zxyvb8icv1pcs31t29n44jfsdl.png)
Complete the question:
A voltage 100 sin wt + 40 cos (3 wt -30°) + 50 sin (5ot + 45°) V is applied to the pressure coil circuit of a wattmeter and through the current coil is passed a current of 8 sin oot + 6 cos (5 wt-120°) A. Find the amplitude and phase angle of the current in order to analyze the circuit.