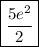Answer:
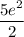
Explanation:
Differentiation is an algebraic process that finds the slope of a curve. At a point, the slope of a curve is the same as the slope of the tangent line to the curve at that point. Therefore, to find the slope of the line tangent to the given function, differentiate the given function.
Given function:
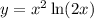
Differentiate the given function using the product rule.
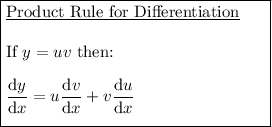

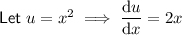

Input the values into the product rule to differentiate the function:

To find the slope of the tangent line at x = e²/2, substitute x = e²/2 into the differentiated function:
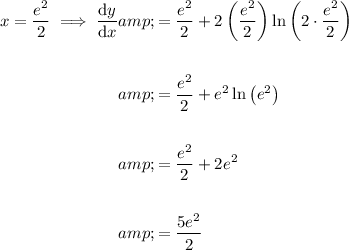
Therefore, the slope of the line tangent to the graph of y = x²ln(2x) at the point where x = e²/2 is: