The tadpole swims across the pond at a velocity of 4.50 cm/s, and the tail exerts a force of 28.0 mN to overcome drag forces.
Velocity of the tadpole, v = 4.50 cm/s
Force exerted by the tail, F = 28.0 mN
To understand the relationship between force, velocity, and drag, we can consider the following equation:
F = k * v
Where:
F is the force exerted by the tail
k is a constant factor
v is the velocity of the tadpole
In this scenario, the force exerted by the tail is given as 28.0 mN, and the velocity is 4.50 cm/s. We can rearrange the equation to solve for the constant factor:
k = F / v
Substituting the given values:
k = (28.0 mN) / (4.50 cm/s)
Now, let's convert the units to a consistent form. Converting 28.0 mN to N:
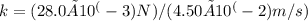
Simplifying, we get:
k = 6.22 Ns/m
Therefore, the constant factor k is equal to 6.22 Ns/m.
This constant factor represents the drag coefficient, which describes the resistance of the water to the motion of the tadpole. It quantifies the relationship between the force exerted by the tail and the velocity of the tadpole. The larger the drag coefficient, the more resistance the tadpole experiences while swimming.
To know more about