Answer: The value of the equilibrium constant is K = 191.
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given the reaction:
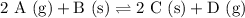
To determine the equilibrium constant, we need the concentrations of each substance at equilibrium.
We can easily determine the concentrations of the solid substances:
![[B] = 4.18 \text{ mol} / 10.0 \text{ L} = 0.418 \text{ M}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/qqw7olwua4cj3s3fitfbt3xsohf8ml090l.png)
![[C] = 6.25 \text{ mol} / 10.0 \text{ L} = 0.625 \text{ M}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/xt9l3t3avw0240f7swvhwzu5wpsrxn9ona.png)
For the gaseous substances, we need to convert the given pressures into number of moles. This can be done using the Ideal Gas Law:

or, rearranged for the number of moles:
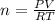
We will use the gas constant value of
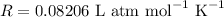 .
.
Then, we have:

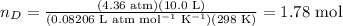
Using our newly found number of moles, we can calculate the concentrations of the gaseous substances:
![[A] = 0.295 \text{ mol} / 10.0 \text{ L} = 0.0295 \text{ M}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/r4vo2y6htbd4n7xwgvc0d2swu5z8s44zin.png)
![[D] = 1.78 \text{ mol}/10.0 \text{ L} = 0.178 \text{ M}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/xvgj74fxqailb0vdr3fj44llq91voyv2sd.png)
Finally, taking everything together, and paying attention to our chemical reaction coefficients, we calculate the equilibrium constant:
![K_c = ([C]^2[D])/([A]^2[B]) = ((0.625)^2(0.178))/((0.0295)^2(0.418)) = 191](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/college/5v5yqu4ztctt885e6t1nktdoi4a9stm6ms.png)