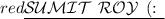The correct answer is (3) their bodies maintain a constant internal temperature.
Warm-blooded animals, also known as endotherms, have the ability to regulate their body temperature internally. They can maintain a relatively stable and constant body temperature regardless of the temperature of their surroundings. This is achieved through various physiological mechanisms such as metabolic heat production, insulation (such as fur or feathers), and cooling mechanisms (such as sweating or panting) to dissipate excess heat.
In contrast, cold-blooded animals, also known as ectotherms, do not have the ability to internally regulate their body temperature. Their body temperature is primarily determined by the temperature of their surroundings. Therefore, option (2) is incorrect, as warm-blooded animals do not have the same temperature as their surroundings.
Option (1) is also incorrect, as the blood temperature of warm-blooded animals can vary to some extent, depending on the specific species and environmental conditions. However, their bodies actively regulate and maintain a constant internal temperature within a narrow range, typically higher than the surrounding environment.
Option (4) is incorrect, as warm-blooded animals do not maintain a constant external temperature. Their bodies strive to maintain a constant internal temperature, even if it means producing heat or utilizing cooling mechanisms to achieve that balance.
Hence, the most accurate statement is that warm-blooded animals are called warm-blooded because their bodies maintain a constant internal temperature, as stated in option (3).
♥️